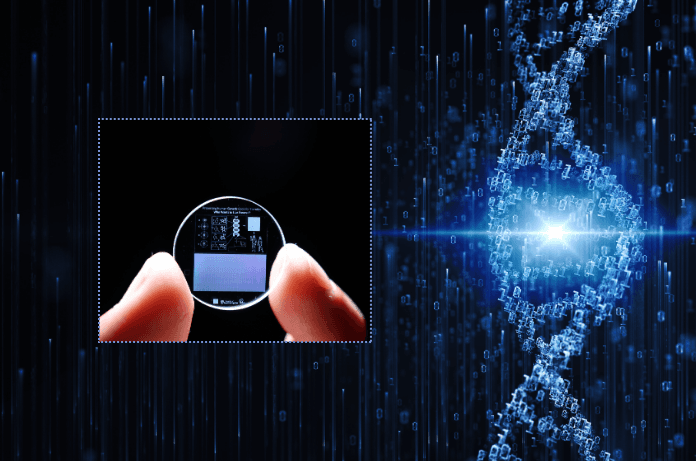
Scientists at the University of Southampton have successfully preserved the entire human genome on 5D memory crystals, a cutting-edge data storage medium with a billion-year shelf life. If science permits, the team believes the crystal may offer a blueprint for saving humanity from extinction for decades, millions, or even billions of years.
The method has the potential to provide a permanent archive of the genomes of threatened plant and animal species.
The Science Behind 5D Memory Crystals
The Optoelectronics Research Center (ORC) at the University of Southampton created the 5D memory crystal.
5D memory crystals can store up to 360 terabytes of data (in the largest size) without losing any data for billions of years, even at high temperatures, in contrast to existing data storage formats that deteriorate over time. As the most durable data storage substance, it holds the 2014 Guinness World Record.
The crystal is the same as fused quartz, among the materials on Earth with the highest chemical and thermal durability. It is resilient to temperatures as high as 1,000°C, fire, and cold conditions. The crystal is also resistant to long-term exposure to cosmic radiation and can tolerate direct impact forces of up to 10 tons per cm2.
Potential Applications of 5D Memory Crystals
The 5D memory crystal is a significant development in data storage technology. These crystals can store up to 360 terabytes of data (in the most critical size) for billions of years without degrading, even in scorching environments, in contrast to standard formats that decay over time. It was awarded the title of the most durable storage material by Guinness World Records in 2014.
The crystal is one of Earth’s most thermally and chemically stable solids, similar to fused quartz. Researchers have shown it can tolerate frigid temperatures, fire, and heat up to 1000°C. It also withstands lengthy exposure to cosmic radiation and direct impacts of up to 10 tons per centimeter.
With feature sizes as small as 20 nanometers, the Southampton team uses ultra-fast lasers to engrave data into nanostructured gaps within the silica.
The team emphasizes that this approach encodes information utilizing two optical dimensions and three spatial coordinates, establishing the “5D” data storage format, in contrast to standard data storage, which uses surface-level marking.
5D’s Environmental Impact
5D memory crystals are a following-generation data storage solution that can store much more data packed at much higher densities on tiny crystals that are highly durable. Apart from the enhancement of technologies above crystals, they also possess a great potential for solving environmental problems affecting traditional data storage methods.
Another advantage of 5D memory crystals, which are incontestably environmental, is their ability to cut energy costs. As opposed to the HDDs or SSDs that require constant power to preserve the recorded data, the 5D crystals are the passive storage solutions.
The phenomenon of 5D memory crystals provides the storage of larger volumes of data in comparably less space due to the extremely high data storage density. Data centers can employ fewer servers and storage equipment, minimizing physical resources and environmental effects.
These crystals, therefore, provide a better and more environmentally friendly solution to storing data by using less energy, having a smaller physical presence, and having a considerably longer lifespan than the standard storage devices we have today. Since 5D memory technology is in its developmental stage, it can take center stage in interrelating climate change and resource depletion challenges.
The Future of 5D Memory Chip
The Memory of Mankind archive and the human DNA crystal are kept in the world’s oldest salt cave. As the mountain moves, the salt mine will eventually naturally close, giving the crystal a stable and secure environment. Because salt is soft, it won’t harm the crystal, keeping it safe for millions of years until future civilizations find it. According to Kazansky, the human genome is protected by this storage technique for an extended period. The University of Southampton group now focuses on preserving DNA from other creatures, like microbiomes and endangered species.
Professor Kazansky said, “This could significantly contribute to the conservation of biodiversity and offer a means to preserve biological information for medical research, genetic studies, and future generations.” Furthermore, we are looking into the potential for storing individualized medical data, which may be helpful in precision medicine and other future healthcare applications. 5D memory crystals are the perfect medium for keeping priceless biological data that may prove vital because of their strength and longevity.
Conclusion
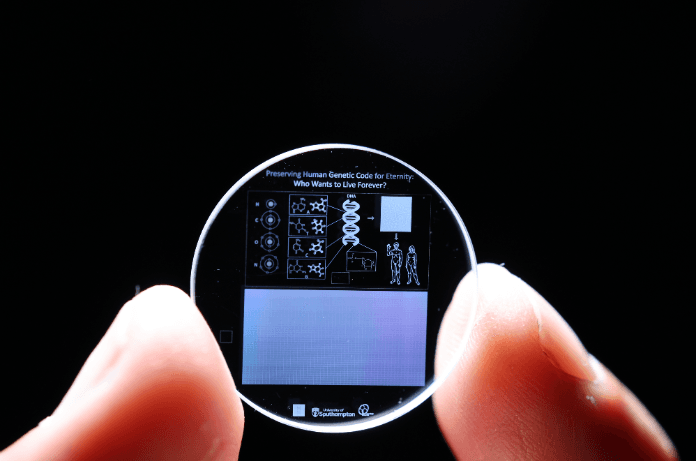
The researchers successfully encoded the entire human genome into the 5D crystal to illustrate the idea. Each of the three billion letters in the genome was sequenced 150 times to ensure accuracy. The crystal is in the Memory of Mankind repository, a specially constructed time capsule found in Hallstatt, Austria, within a salt cave.
This ground-breaking memory crystal provides a means of storing data for billions of years, opening up new possibilities for data storage in the future. 5D memory crystals present many opportunities for technological improvement due to their unparalleled durability and data density. However, their broad use also raises important ethical issues that must be properly considered.

